
Reliable Car Transportation Services: Get Your Vehicle Moved Safely
Additionally, we provide high-end and luxury moving assistance for buyers that require careful handling, inspection, and attention to detail, depending on the season and vehicle type.
Best Transit Booking System
We understand that communication is key, so to understand clients, we provide a user-friendly booking system that enables you to communicate with each other and with us. This system ensures that all your hauling needs are met within the shortest time possible, including specific route planning to optimize the loads and area coverage so there are no delays. This solves the communication issue faced by most customers.
Now, you don't have to worry about booking appointments by phone or sending emails and waiting for a reply. Our services operate in hundreds of cities across the US, including Cincinnati, Columbus, Delaware, and many others. We also offer motorcycle conveyance assistance and snow-proof vehicles for the winter season.
Affordable Conveyance Price
Pricing can be a significant issue when it comes to auto-moving. Our pricing is affordable and tailored to your budget, and we also provide dealership delivery solutions for your products.
You can contact us for more information on our services and pricing through our phone number, and we will provide you with the latest ratings and proof of our work. You can also Get a Free Pricing Quote to haul your next vehicle.
As community residents, we understand the need for reliable and trustworthy car haulage assistance. We take pride in doing an excellent job every time, regardless of the length of the journey or the window of time for delivery.
Customer Satisfaction
Our kindnesses have been used by thousands of satisfied customers who can attest to the high quality of our work. We are the right firm for the job if you need to move your vehicle quickly to its destination or origin.
Our advanced system and commitment to excellence make us the best choice. Our Transport FAQs section can answer any questions you may have.
You can contact us from anywhere, and our A+-rated office has the solution for your shipping needs. Hurry up, book now, and your ride delivery will be the most straightforward you've ever had!
Types Of Vehicle Shipping Solutions
The standard moving benefits include:
- Open-Air Auto Freight
- Enclosed Transit
- Terminal-to-Terminal
- Door-to-Door Transport
- Luxury, Exotic and High-End Shifting
- Electric Vehicle Shipping
When managing yourbusiness and having a reliable company, your business soloists don't have reasonable delivery assistance that can handle various situations and routes, regardless of package weight or size. Additionally, they should offer key features such as real-time tracking and scheduling options to ensure your deliveries are on time.
When choosing a delivery assistance, it is essential to business the items you are dispatching and your business needs. Some delivery benefits specialize in handling fragile or high-value items, while others excel at bulk deliveries. The exemplary Service for you will depend on your particular situation and requirements.
In addition to the standard features of reliable conveyance and on-time delivery, you may look for additional features such as parcel insurance and signature confirmation for added peace of mind. With exemplary delivery assistance, you can rest assured that your packages will arrive safely and on time, no matter what challenges may arise along the way.

Open Carrier Hauling
Open carrier transport is the most popular and cost-effective way to ship vehicles across the country. Your car, SUV, or truck is transported on an open trailer, ensuring a fast and efficient delivery at an affordable price. This is a great option for standard vehicles and is widely used for its reliability and accessibility.
Enclosed Auto Transport
For those seeking extra protection, enclosed auto transport offers the ultimate safeguard against harsh weather and road conditions. This premium service is ideal for luxury, antique, and classic vehicles, ensuring they arrive in pristine condition. We offer two types of enclosed transport: soft-sided and hard-sided.
Soft-Sided Enclosed Transport
Soft-sided trailers are covered with durable canvas or vinyl, shielding your vehicle from dirt, debris, wind, and rain. While they provide more protection than open transport, they may not completely block out extreme weather fluctuations.
Hard-Sided Enclosed Transport
For maximum security, hard-sided enclosed transport is the gold standard. Your vehicle is fully enclosed, keeping it safe from road hazards, weather, and prying eyes—perfect for high-end or collectible cars that require extra care.
Why Choose Hard-Sided Enclosed Transport?
- Full Protection – Your car is completely sealed off, shielding it from road debris, dust, and extreme weather.
- Privacy & Security – Ideal for high-value vehicles, keeping them out of sight during transit.
- Hassle-Free Process – We handle all the paperwork and logistics, ensuring a smooth shipping experience.
Choosing between soft-sided and hard-sided transport depends on your vehicle's needs and your level of protection preference. Both options provide peace of mind throughout the shipping process.
We Ship Nationwide & Worldwide!
Get a FREE, no-obligation quote today! Click below or call 1-888-230-9116 to get started.

Terminal-To-Terminal
Terminal-to-terminal delivery is the industry standard for transporting vehicles. It requires the customer to drop off and pick up their car from a depot or terminal.
Open-air terminal-to-terminal delivery is the most affordable Service currently available.
To offer our customers the best, our company maintains terminals in nearly every major city in the United States. If a terminal is inaccessible, door-to-door transit is always an option.

Door-To-Door Facilities
Door-to-door shifting costs more than terminal-to-terminal dispatching but can save considerable time when hauling your vehicle across the country.
Advantages Of Door-To-Door Vehicle Moving
The advantage of door-to-door vehicle donating is that you don't need to drop off or pick up your vehicle at a terminal; we do not need you. It doesn't need to be at the specified notation, and you don't need a broker.
Sometimes, our transfer carriers may encounter difficulty navigating certain areas. In such cases, we rely on the expertise of our trusted truck drivers to handle all the logistics and ensure a smooth and hassle-free conveyance experience. Our usefulness boasts a versatile fleet of specialized carriers capable of handling any logistical challenge.
If there are navigational obstacles, our experienced drivers will coordinate with you to determine the most convenient location for pickup and drop-off. Rest assured that your vehicle will be hauled safely and securely to its destination.

Exotic And Luxury Vehicles
When transporting an exotic, classic, or luxury vehicle to Hawaii, North Carolina, New York, Dayton, Los Angeles, New Mexico, Washington, California, New Jersey, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, or Illinois, you want to be sure that your vehicle will be handled with the utmost care and arrive in the same condition it was left in.
Upon request, we can even load your mobile into the first position in the shipping trailer so it does not undergo loading and unloading as other cars are added and removed safely. There's a luxury motor stay.
Luxury Vehicle Delivery Insurance
Though sending insurance and satellite tracking are standard with every quote we offer, it's essential to consider additional insurance if your vehicle is particularly valuable. This type of insurance can be provided through your existing auto insurance plan or purchased through a third-party carrier.
Assistance By Dispatching Firms For High-End Vehicles
Here are some of the benefits offered by hauling companies for high-end vehicles:
- Air ride" "suspension prevents" "huck check-in, a smoother ride, and easy haul
- Wall and floor-mounted brackets are used for a more secure fit
- Covered interior and exterior, even with enclosed easy-shift
- Hydraulic lift gate used for"t "e safest carriers''"loading and unloading possible
- Drip guards to prevent potential leaks during transit
- Equipment designed to handle a wide range of vehicle types
Affordable Vehicle Carriage Solution
Are you a veteran looking for an affordable and reliable carriage service? Look no further than our motor hauling cost calculator. Our online calculator helps you compare quotes from multiple transit companies to ensure you get the best prices for your ride loads.
With our online car shipping calculator, you can trust that your vehicle will be moved with the utmost care and delivered safely to your destination, regardless of weather conditions or other elements affecting conveyance.
Moreover, several haulers compete for your business, so you can rest assured that you get the most competitive and affordable conveyance quote. If you are a veteran, you may even be eligible for a discount on the fee. Please visit the links provided on our website for more information.
Easy Quotations
The steps provided are straightforward. Most transit quotes require customers to provide the name, model, and year of manufacture of their vehicle and the transport type. If you have any questions about the process or need any guidance, our team is always available to assist you.
The rise of online logistics calculators directly results from the ability to provide cost-effective and reliable solutions for the seamless delivery of goods to their intended destinations.
In our modern age of convenience and efficiency, delivery assistance has become an indispensable resource for individuals and businesses, providing a reason to rely on them for all their logistics needs.
Car Hauling For Students
Additionally, if you are a college student looking for a way to shift your vehicle back home during breaks, delivery can help you. The law requires that all cars being moved must be insured, and our carrying cost calculator ensures that you get the best insurance coverage available.
So, why wait? Try our online transmitting calculator today and start saving on your auto cargo!
Movers Near Me
Car transporters provide convenient and reliable carriers for vehicles. These services are commonly used when moving long distances or shipping cars to different locations.
Choosing Reliable Assistance
Over 90% of users report high satisfaction with the convenience and reliability of the Usefulness.
By choosing a trusted vehicle delivery assistance, owners can rest assured that their investment is in good hands. This also frees them up to focus on other essential tasks. A professional enterprise pays close attention to even the most minor details during the conveyance process, ensuring minimal damage to the vehicle.
Easy Insurance Claims
In case of any severe damage, the insurance will cover the costs, and any damaged part of your vehicle will be repaired. You can easily file an auto transport damage claim.
Environment-Friendly Transit
Additionally, movers help reduce carbon emissions by 25% annually, making them an environmentally friendly option. If you have to travel long distances, you can choose to drive your vehicle there.
However, doing so risks accidents or other mechanical failures on the road. Depending on your destination, you might be driving for quite some time. Sure, insurance might cover the cost of damages, but all the time and effort it takes to prepare the ride for such a journey is a headache.
Missional Facilities
It is much easier to hire a professional assistant to handle everything. High-end benefits will even allow you to track the location of your vehicle and add extras to the carrier to ensure that your motor comes out as immaculately as it went in. Not only will you have that guaranteed you'll mind, but you'll also save money on the bargain and price lock promise.
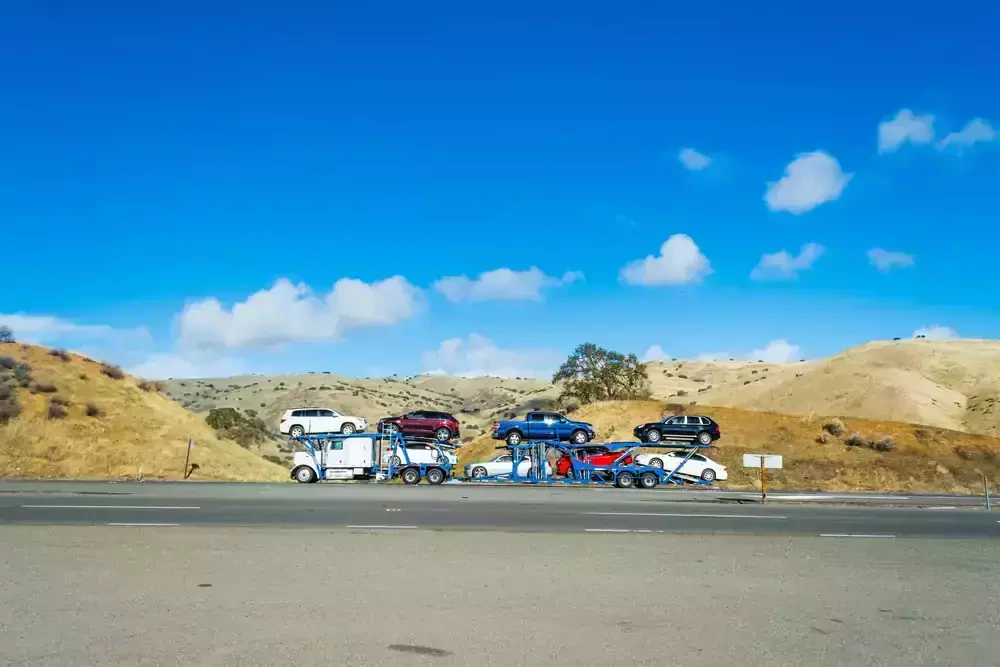
Transit Categories
Motor haulage can fall under several categories depending on the moving company that moves the ride. Vehicle assistance may use several carrier methods to get a vehicle from one point to another. Among the most common methodologies are:

Rail Freight
These companies focus on transporting mobiles using the vast interconnected rail network around the US. They are either moved open-air or within car transporting a pretty quick way of getting a vehicle from one point to another that homes with. Moving an automobile comes quickly; because of the complexities of rail transit, not every delivery company offers rail freight as an option.
Air Carriers
Another type of moving assistance is air freight. This is the fastest way for transit companies to move from one place to another, regardless of where in the USS they are.
Unfortunately, air freight is expensive and may cost quite a lot, depending on where the mobile needs to fly. However, it is also the safest method of moving a vehicle, and with so many airports nationwide, it's easy to find a landing location near you.
Truck Conveyance
A standard taxi is one of the most common vehicle conveyance services you'll find is a standard taxi. It's a no-frills way to move a car, and it takes a while, but the vehicle gets to its destination safely and soundly. A standard taxi is a phone number and the most convenient method of moving between locations.
Depending on the destination,, the truck can reach the final point before the owner receives the cargo, limiting the driving needed.

Vehicle Conveyance When Relocating
Considering the vast number of people currently relocating and looking for interstate car transport solutions, an invaluable asset to many moving companies. The number of people moving in the last year has risen, including those who need to move their vehicles.
The mental and emotional toll of relocation, with all its associated details, like arranging for moving expensive vehicles, can make it challenging to focus on —people who need to relocate but are unsure of how they can benefit from using mobile conveyance assistance.
Best Drivers For Relocating
Most haulers in Ohio and Cleveland also provide a concierge solution to pick up and drop off the vehicle, reducing the amount of driving the owner must do. The drivers of these vehicles are highly skilled experts who analyze the vehicle's safety.
Good vehicle delivery facilities already understand the need to deliver clients' vehicles on time. Many shifting companies offer daily updates on a car's progress to ensure the owner always knows where it is.
Choosing an auto-delivery firm is the best bet for long drives, as there is a much higher chance of something going wrong. It will ensure that the vehicle isn't driven over those massive distances.

What to Look for in a Reliable Auto Transport Company
Finding the right vehicle transport company isn’t as simple as a quick Google search. With so many options out there, choosing a provider that actually delivers on its promises takes a little research. Here’s what really matters.
Price vs. Quality
Cheap isn’t always good. Low prices often mean cutting corners, whether it’s weak insurance, slow delivery, or poor customer support. A reliable company offers fair, transparent pricing without sacrificing quality.
Reputation Matters
Reviews tell the real story. Look at Trustpilot, Google, and BBB to see what past customers say. Consistent positive feedback on safe, timely delivery and good communication is a green flag.
Licensed and Insured. No Exceptions
Any legitimate transport provider must be licensed, bonded, and insured. Before booking, check their USDOT and MC numbers. This ensures they meet industry regulations and that your vehicle is covered in case of unexpected issues.
Tracking and Communication
It’s not just about location. Proximity to a transport company doesn’t always mean better service. What really matters is their ability to keep you informed. A good company provides real-time tracking and clear updates so you always know where your car is.
Safe and Reliable Transport Options
Not all shipping methods offer the same level of protection. Open transport is great for standard vehicles, while enclosed transport is best for luxury or classic cars. The cheapest option isn’t always the safest, so choose what works best for your needs.
Customer Service and Professionalism
A company that values its customers won’t leave you guessing. They’ll answer your questions, explain their process, and provide accurate quotes without surprises or hidden fees. If they’re hard to reach or vague about their services, take that as a warning sign.
A Modern and Professional Website
A serious auto transport company should have an up-to-date, easy-to-navigate website. If their site is outdated or missing key details like service options and pricing, it’s a sign they might not be as reliable as they claim.
Ship with Confidence
Moving your car is about more than just getting it from point A to B. It’s about trust and peace of mind. Take the time to research your options, ask the right questions, and choose a company that puts your vehicle’s safety first.
Get a Free Quote Today
Need a reliable auto transport partner? Contact A-1 Auto Transport for a hassle-free experience.
📞 Call 1-888-230-9116 for a free, no-obligation quote.

Pickup And Delivery Process
A trusted car shipping company delivery assistant will secure your vehicle to its final location. You'll be treated to regular updates on transit via phone, which will keep you informed every step of the way. If you have complaints, you can quickly contact friendly and helpful staff. The cost of your transportation solutions will vary depending on your chosen moving method.
Some methods operate faster than others, offering quicker delivery at a higher price. A delivery usefulness might even have a truck driver who will deliver your vehicle to your door. When you consult them about a quote, ask about their concierge assistance.
Ensure your delivery service provider has cargo insurance if anything happens during transit. While most auto carriers are, there's no telling what could happen. It's better to be prepared. Choosing a professional delivery solution that respects its former clients is crucial to getting the best value for your money.
Ensure the signal arrives safely by hiring a reliable transport provider like us. We offer dependable vehicle hauling solutions and provide shipping estimates.
Vehicle owners can gain a lot from using moving kindnesses. Insurance vehicles during transit, two pickup and delivery assistance around the clock, and as-you're-pocket costs are just a few perks. Moving assistance can also transfer vehicles across international borders. When you work with a professional conveyance company, you can have peace of mind knowing that your ride will arrive pristine. Professional movers use cutting-edge safety gear to safeguard your vehicle during transit.
Low-Cost Repositioning
We are an excellent choice if you need to shift cheaply. We employ a team of trained moving professionals and have offices and warehouses in major cities across the United States and worldwide. Our flexible payment options cater to students and those on a tight budget.
We transport vehicles between airports or from your door to ours, including high pickups and luxury cars. Our team is ready to assist you in scheduling your move.
Your SUVs, trucks, or motorcycles will arrive without scratches, dents, or added mileage. Upon arrival, inspect your vehicle. If you find any damage, notify the delivery representative before leaving.

Helpful Tips

Relevant Statistics
- Over 90% of car transportation assistance in major cities boasts a punctuality rate of 99.9%.
- The average wait time for a conveyance usefulness is less than 5 minutes.
- More than 80% of carrier kindness providers offer a cashless payment option.
- Conveyance usefulness has reduced carbon emissions by approximately 30% in the past decade.
- 95% of passengers using carrying benefits report feeling safe and secure during their rides.
General Facts
- Auto moving assistance provides professional moving and delivery.
- These usefulness are commonly used f or hauling vehicles across long distances, such as interstate or international loads.
- Car haulage kindnesses ensure the safety and security of vehicles during transit.
- Pickup has various options for haulage, including open transit or enclosed shifting.
- Transit benefits often provide door-to-door pickup and delivery, making it convenient for customers to dispatch their vehicles.

Frequently Asked Questions
What types of car transportation services does A-1 Auto Transport offer?
We provide a full range of vehicle shipping services, including open carrier, enclosed carrier, door-to-door delivery, terminal-to-terminal options, and international transport. Whether you’re moving a daily driver, classic car, motorcycle, or RV, we tailor every shipment for safety and timing. Learn more about our door-to-door auto transport options for the most convenient pickup and delivery.
How much does car transport cost in 2025?
Average U.S. auto transport rates range from $500–$1,500, depending on distance, vehicle size, transport type, and season. Open carriers are most affordable, while enclosed carriers cost 30–50% more for added protection. For example, shipping a sedan coast-to-coast may cost around $1,200, while regional moves typically stay under$600. Get an instant rate using our car shipping cost calculator.
How long does it take to ship a car?
Typical delivery times range from 2–9 days, depending on route distance, weather, and carrier availability. Short hauls under 500 miles can arrive in 1–3 days, while coast-to-coast trips may take up to a week. We’ll provide real-time tracking and estimated delivery windows when you book. For guaranteed or express delivery, see our same-day auto transport options.
Should I choose open or enclosed transport?
Open transport is the industry standard and the most cost-effective method for most vehicles. Enclosed transport provides complete protection from weather, road debris, and prying eyes — ideal for classic, luxury, or high-value cars. Enclosed shipping typically adds 30–60% to the cost but offers the highest level of care. Visit our enclosed car transport guide to learn which option best suits your vehicle.
Is my car insured during shipping?
Yes. Every carrier working with A-1 Auto Transport carries FMCSA-mandated cargo insurance, protecting your car against damage during transit. Coverage applies from pickup to drop-off. Before shipping, we perform a full inspection and document your car’s condition on the Bill of Lading for transparency and peace of mind.
How far in advance should I book my shipment?
Booking 1–2 weeks in advance usually ensures the best price and carrier selection. During busy seasons (summer or holidays), earlier booking gives you more flexibility. However, we can often arrange same-day or next-day pickup in major metro areas through our expedited auto transport service.
Can A-1 Auto Transport ship cars from dealerships or online purchases?
Absolutely. Whether you’ve bought a car from a local dealer, Carvana, eBay, or an out-of-state auction, we can handle pickup directly from the seller. Working with A-1 directly helps avoid dealer markups or storage delays, and we coordinate with both parties to ensure a smooth, secure transfer.
Do I need to be present for pickup or delivery?
Either you or a designated representative must be present to sign the Bill of Lading during pickup and delivery. This confirms vehicle condition and ensures a transparent chain of custody. If you can’t attend, simply authorize a trusted person, such as a family member, neighbor, or friend, before the carrier’s arrival.
What paperwork is required to ship a vehicle?
You’ll need your Bill of Lading, insurance terms, and, in some cases, photo ID or title documentation. The Bill of Lading serves as your contract and proof of vehicle condition at pickup. Depending on your state and lienholder, additional authorizations may be required. You can review documentation examples on our auto transport paperwork guide.
Can I leave personal items in my car?
Most carriers allow up to 100 lbs of personal items, typically stored below window level in the trunk. Heavier or valuable items are discouraged because they aren’t covered under cargo insurance and may affect the vehicle’s weight. Keeping your car light, clean, and easy to inspect speeds up the pickup and delivery process.
What happens if my car is damaged during transport?
In the rare event of damage, note it immediately on the Bill of Lading and contact our claims team. A-1 Auto Transport assists with filing directly through the carrier’s insurance. Claims typically resolve within 7–14 days, depending on the extent of review and documentation. For guidance, visit our auto transport damage claim guide.
How can I track my shipment?
We provide GPS tracking and regular updates from pickup to delivery. You’ll receive notifications by email or text, and you can check real-time progress anytime. Learn how to use our tracking tools on the car shipping tracker page.
Do you ship vehicles internationally?
Yes. With over 20 years of global logistics experience, A-1 handles overseas car transport by container, Ro-Ro, or air freight. Our international team manages customs paperwork, port coordination, and delivery to more than 190 destinations. Learn more about routes and pricing on our international car shipping page.
What payment options are available?
We accept major credit cards, wire transfers, and certified checks for convenience. A small deposit is typically due upon booking, with the balance paid at delivery. Payments are fully transparent — no hidden fees or surprise surcharges.
What are the main benefits of shipping instead of driving?
Car shipping saves time, mileage, and wear on your vehicle. It’s safer than long road trips, especially across multiple states or during winter. You avoid hotel, fuel, and toll costs while professional drivers ensure secure delivery. Many customers use our service for relocations, online purchases, or seasonal moves.
Can I ship more than one type of vehicle or equipment in the same order with your car transportation services?
Yes, you can ship different types of vehicles or equipment in a single order using our car transportation services. We work with a network of carriers that can handle everything from standard cars and SUVs to motorcycles, boats, heavy equipment, and more. When you provide details about each item such as make, model, weight, and any special attachments; we’ll match you with the right carrier for your full shipment.
Keep in mind that shipping multiple types of vehicles or equipment may affect the timeline or cost because the carrier needs the proper trailer, loading gear, and route planning to accommodate oversized or unique items. Providing full details up front ensures we can give you an accurate estimate and schedule. With one coordinated order, you’ll save time, reduce paperwork, and simplify the logistics of moving multiple items.




 Share on Facebook
Share on Facebook Share on LinkedIn
Share on LinkedIn Share on Twitter
Share on Twitter Google
Google  Instagram
Instagram 



