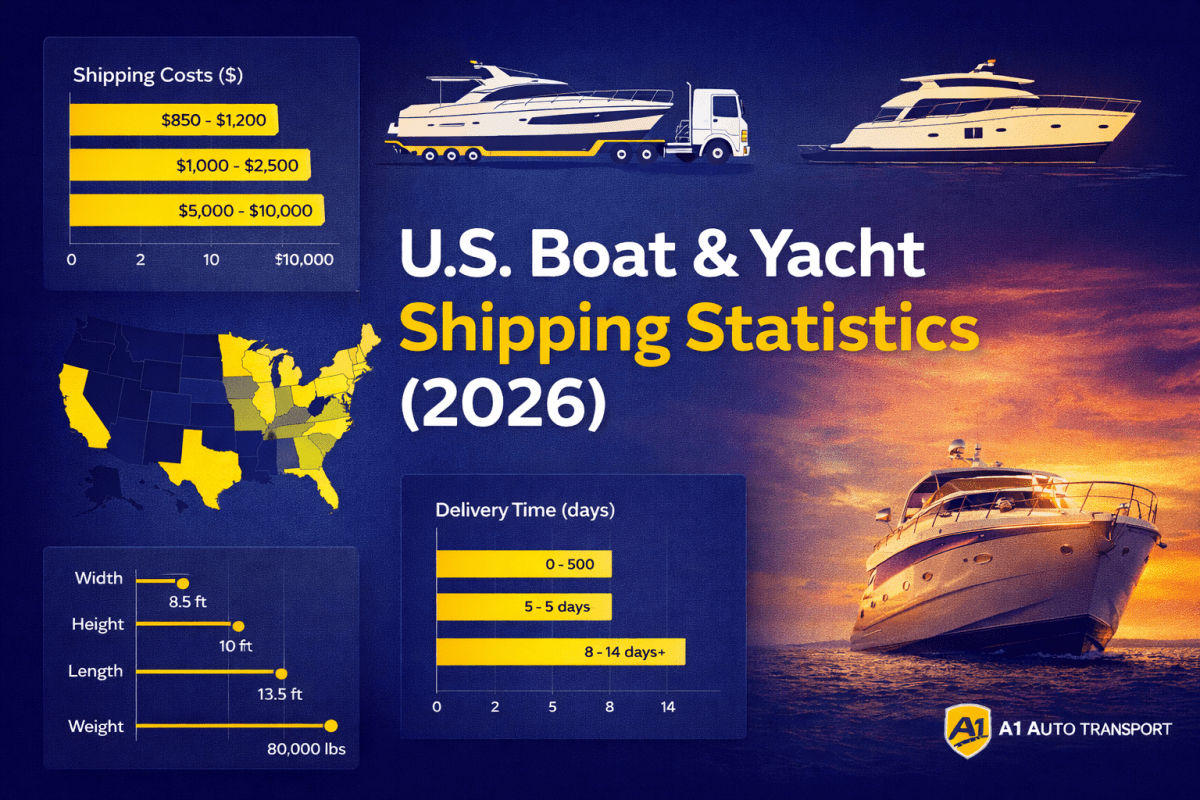
RV & Trailer Transport Statistics: Costs, Delivery & Trends
RV & Trailer Transport Cost Ranges by Distance (U.S.) RV and trailer transport costs in the United States vary primarily by distance, vehicle size, and handling complexity. Compared to standard pa...